
Here are eleven (11) nursing care plans (NCP) and nursing diagnosis (NDx) for fracture: In emergency trauma care, basics include triage, assessment and maintaining the airway, breathing, and circulation, protecting the cervical spine, and assessing the level of consciousness. Performing an accurate nursing assessment regularly allows the nursing staff to manage the patient’s pain and prevent complications.

They are associated with a fall on an outstretched arm. Although Galeazzi fracture patterns are reportedly uncommon, they are estimated to account for 7% of all forearm fractures in adults. Galeazzi fractures account for 3-7% of all forearm fractures. However, in skeletally immature patients such as children, the fracture is typically treated with closed reduction. Nonsurgical treatment results in persistent or recurrent dislocations of the distal ulna. It has been called the "fracture of necessity," because it necessitates open surgical treatment in the adult. Galeazzi fractures are best treated with open reduction of the radius and the distal radio-ulnar joint. Galeazzi fracture after surgical fixation The deforming muscular and soft-tissue injuries that are associated with this fracture cannot be controlled with plaster immobilization. Īfter the injury, the fracture is subject to deforming forces including those of the brachioradialis, pronator quadratus, and thumb extensors, as well as the weight of the hand. If the fall is on the outstretched hand with forearm in pronation, the dislocation is dorsal, and if forearm is in supination at the time of injury, the dislocation is volar. The dislocation of ulnar head in Galeazzi fracture dislocation may be dorsal (commoner) or volar (rare) depending on the mechanism of injury.
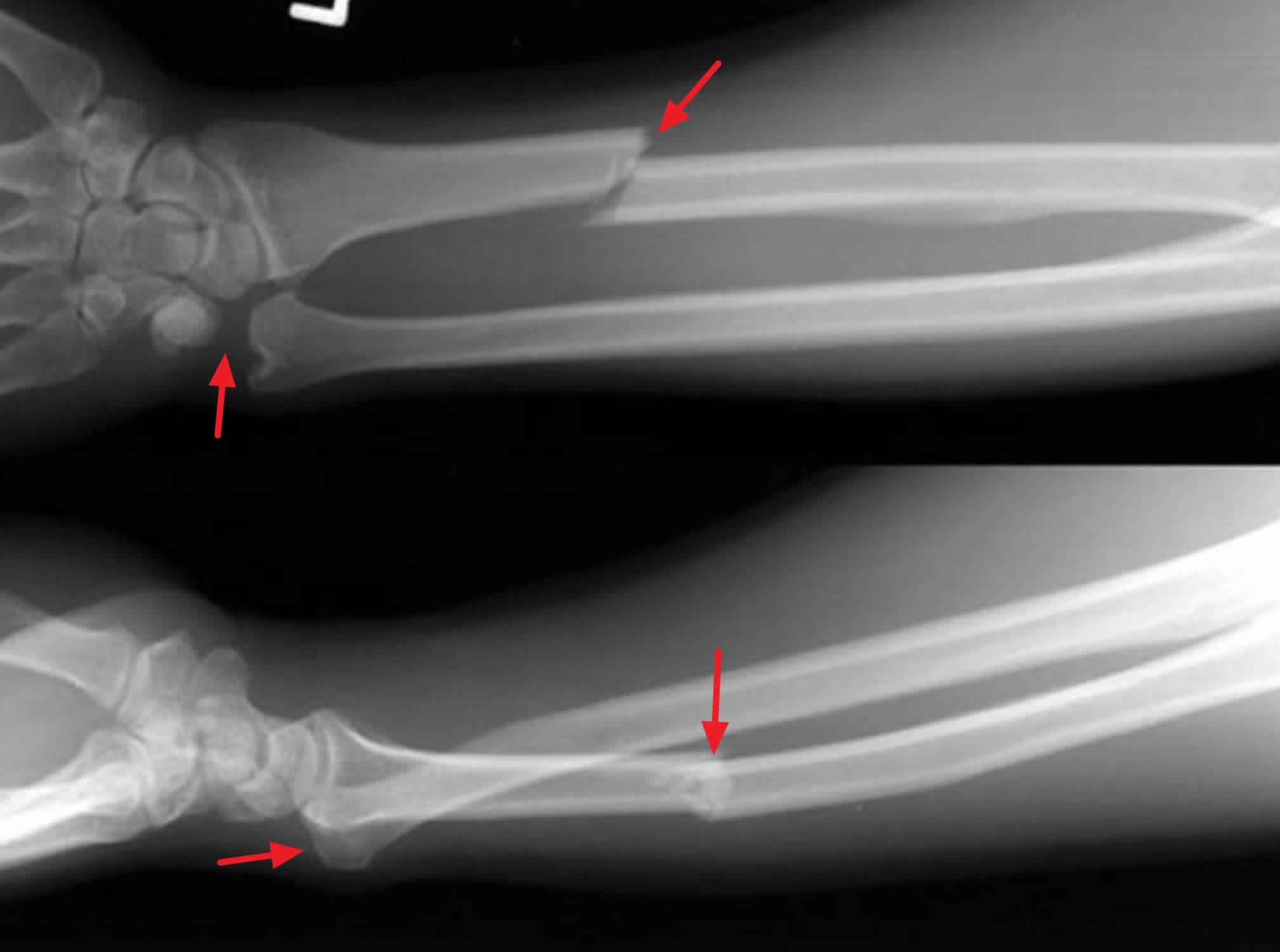
Galeazzi fractures are sometimes associated with wrist drop due to injury to radial nerve, extensor tendons or muscles.
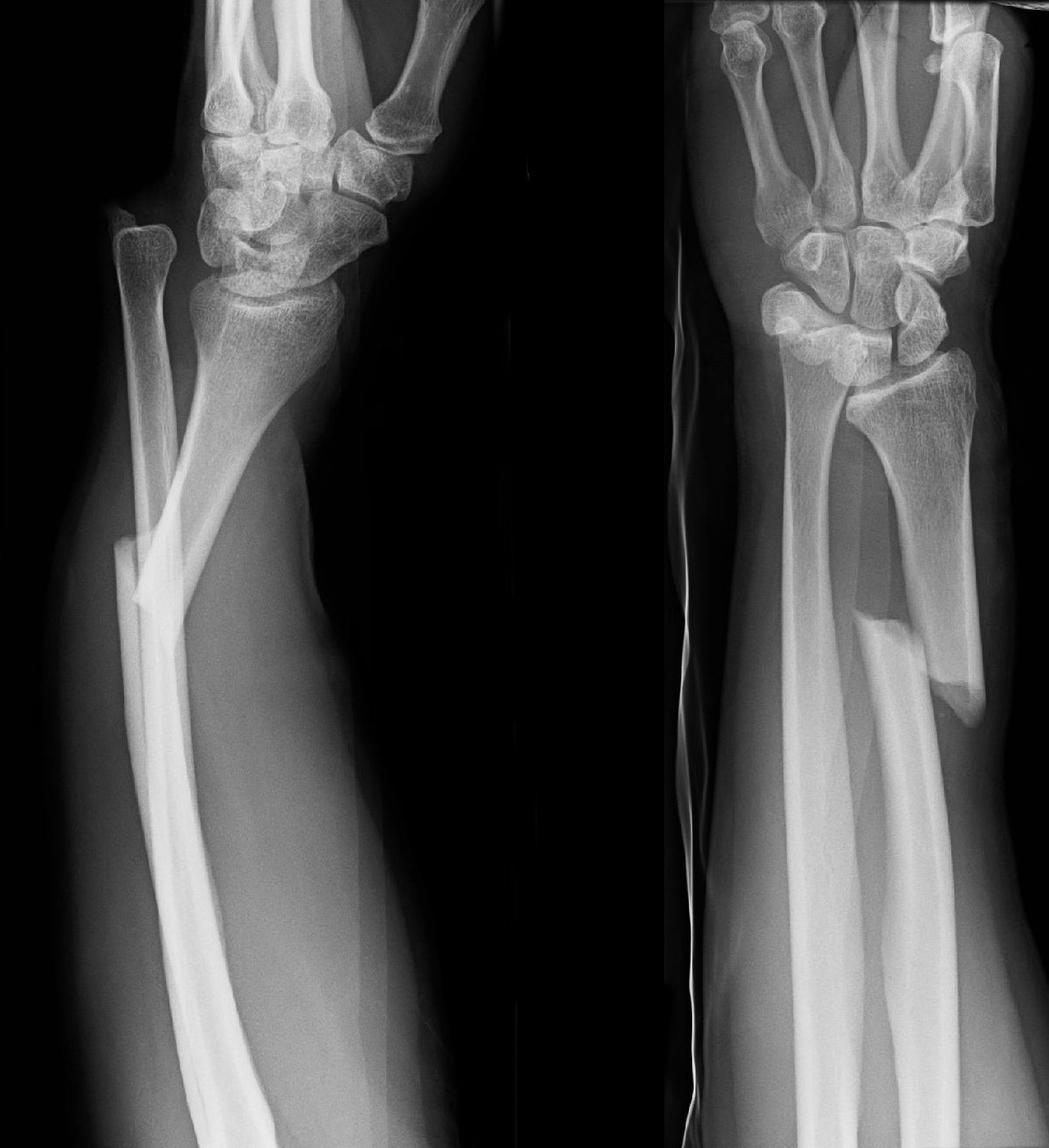
Injury to the AIN can cause paralysis of the flexor pollicis longus and flexor digitorum profundus muscles to the index finger, resulting in loss of the pinch mechanism between the thumb and index finger. A purely motor nerve, the AIN is a division of the median nerve. Anterior interosseous nerve (AIN) palsy may also be present, but it is easily missed because there is no sensory component to this finding. Forearm trauma may be associated with compartment syndrome. This injury is confirmed on radiographic evaluation. Pain and soft-tissue swelling are present at the distal-third radial fracture site and at the wrist joint. It classically involves an isolated fracture of the junction of the distal third and middle third of the radius with associated subluxation or dislocation of the distal radio-ulnar joint the injury disrupts the forearm axis joint. The Galeazzi fracture is a fracture of the distal third of the radius with dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint. Arrow points at the dislocated ulnar head Medical condition Galeazzi fracture-dislocation


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
